The Role of NAD Therapy in Aging
Research on aging has identified NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) Therapy as a promising option to combat the mechanisms that age our bodies on the cellular level. NAD, is a coenzyme found naturally in the cells of the body and plays a central role in many of the biological processes associated with aging, including cellular energy production, oxidative balance, and communication between cells. Healthy NAD levels help support normal cell function, metabolic efficiency, and resilience to stress—factors that directly influence how our bodies feel and function over time.
For much of human history, aging was viewed as an inevitable process—something that simply happened, with little influence over how quickly or how well we aged. Today, we know that aging is the single greatest risk factor for most chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, neurodegenerative conditions, and cancer.
Modern research now shows that aging is driven by specific biological processes that gradually reduce the function of our cells, tissues, and organs over time. Scientists have identified a set of shared patterns behind this decline, commonly referred to as the hallmarks of aging. These changes affect how cells produce energy, repair damage, communicate with one another, and respond to stress.
Importantly, aging is no longer viewed as a fixed or purely passive process. Growing evidence suggests that the rate and quality of aging can be influenced by internal and external factors such as inflammation, metabolic health, environmental stressors, and cellular energy availability. NAD levels have shown to be a key factor in many of the hallmarks of aging.
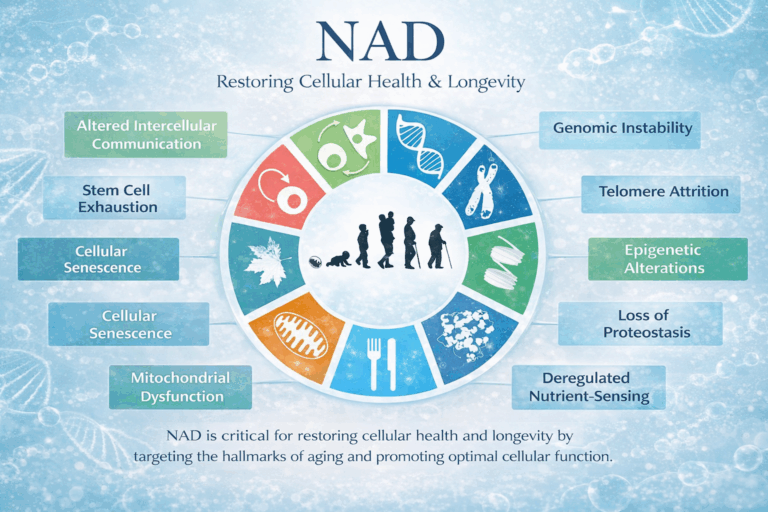
NAD Depletion in The Body
Research has identified several reasons for NAD depletion:
Age: NAD levels naturally decline with age. Research shows levels begin dropping as early as our 20’s, with notable decreases in middle age and continue as we age. This is where we see lower energy production and cellular repair.
Excessive DNA damage (from free radicals): Overtime free radicals can cause damage to our DNA. This process can be aggravated by environmental toxins like:
- heavy metals
- pesticides/solvents
- Mycotoxins
- air pollution (PM 2.5)
NAD levels become depleted when the body has to constantly repair this damage.
Chronic immune activation and inflammatory cytokine production: Ongoing immune activation and chronic inflammatory states demand a lot of the body’s resources and can result in lower levels of NAD. Common contributors:
- Chronic infections (Long Covid, Chronic Lyme, etc..)
- Autoimmune illness
- CIRS or mold illness
- Stress and high cortisol
- Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS)
- Sleep deprivation
How to Increase NAD Levels
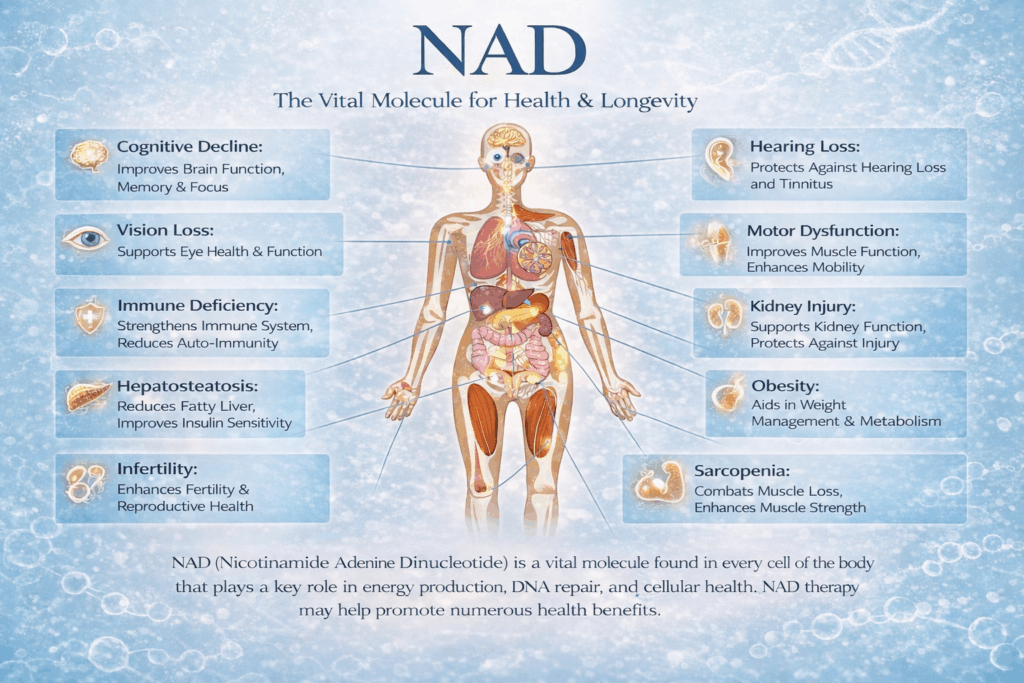
Restoring and increasing NAD levels have shown a positive effect on many age-related disorders resulting from accumulation of chronic oxidative stress, inflammation and impaired mitochondrial function. NAD levels are integral to cell function and are considered a key molecule linked to many of the hallmarks of aging, which are positively influenced by higher levels of NAD availability.
Because NAD levels naturally decline with age and ongoing stressors, many people are now exploring ways to support and restore healthy NAD availability as either a part of a proactive wellness strategy, or to support and repair damage from existing medical conditions.
Benefits of NAD Therapy and Supplementation:
What is The Best Way to Take NAD?
NAD supplementation can come in many forms and the best way to take NAD depends on your goals and preferences. Oral supplements aren’t readily bioavailable, making pill forms most ineffective, while injections and infusions, nasal delivery and lotions bypass the digestive system to reach the bloodstream.
IV therapy will provide the most bioavailable form, allowing for 100% of the molecules to be delivered to the bloodstream. It provides more immediate results and can be delivered at much higher doses. Depending on your goals with treatment, it can offer prolonged and sustainable levels of NAD, resulting in significantly fewer treatments than the alternative delivery methods.
Subcutaneous (Sub-Q) NAD Injections
These can be done in-office by one of our nurses or self administered in the comfort of your own home. It is done with a small injection just under the skin. It provides a slower, more steady increase to NAD levels and can be done supportively with IV therapy or as a standalone therapy.
NAD Nasal Spray
This delivery method uses the nasal passages as a way to bypass the digestive system. Intranasal effectiveness is due to the rich number of blood cells and thin layer of skin protection that allows for easy absorption and circulation through the body. While the nasal spray can be used as supportive with either Sub Q or IV forms, its consistent, stable and convenient delivery can be great for those looking to avoid needles.
NAD Cream
While the NAD is absorbed through the skin and some does make it into the bloodstream, the value of NAD cream goes beyond what any of the other forms we offer can. For people suffering neuropathy, it can bring temporary, but profound relief to symptoms.
As a beauty product it provides a direct delivery to skin cells, providing antiaging benefits. NAD has been found to be integral to the repair systems our skin has in relation to aging and are directly dependent on NAD to perform their function.
Safety and Considerations
Research assessing tolerance of NAD supplementation suggests it is well-tolerated by most individuals, including those with other health conditions. NAD therapy can be a helpful wellness tool, but like any therapy, it works best when it’s personalized, properly administered, and part of a broader health strategy.
Most side effects from NAD come from the particular delivery method and are short-lived. IV Therapy can cause some chest tightness and digestive discomfort when done too fast. Sub Q can cause mild irritation at the delivery site, and nasal administration can cause some irritation for some people.
Please book a 15 minute free consult to discuss which option might be best for you
References and Research:
Rajman L, Chwalek K, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The In Vivo Evidence. Cell Metab. 2018 Mar 6;27(3):529-547. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.011. PMID: 29514064; PMCID: PMC6342515. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6342515/#S20
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013;153(6):1194-217. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3836174/
Braidy N, Berg J, Clement J, Khorshidi F, Poljak A, Jayasena T, Grant R, Sachdev P. Role of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and Related Precursors as Therapeutic Targets for Age-Related Degenerative Diseases: Rationale, Biochemistry, Pharmacokinetics, and Outcomes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Jan 10;30(2):251-294. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7269. Epub 2018 May 11. PMID: 29634344; PMCID: PMC6277084. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29634344/
Conlon NJ. The Role of NAD+ in Regenerative Medicine. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022 Oct 1;150(4 Suppl ):41S-48S. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009673. Epub 2021 Sep 28. PMID: 36170435; PMCID: PMC9512238. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9512238/
Braidy N, Liu Y. NAD+ therapy in age-related degenerative disorders: A benefit/risk analysis. Exp Gerontol. 2020 Apr;132:110831. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2020.110831. Epub 2020 Jan 7. PMID: 31917996. Sharma R, Ramanathan A. The aging metabolome-biomarkers to hub metabolites. Proteomics. 2020;20:e1800407. https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/pmic.201800407
Sharma R, Ramanathan A. The aging metabolome-biomarkers to hub metabolites. Proteomics. 2020;20:e1800407. https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/pmic.201800407Izabelle de Mello Gindri, Gustavo Ferrari, Luiz Paulo S. Pinto, Juliana Bicca, Isis Kelly dos Santos, Darlan Dallacosta, and Carlos Rodrigo de Mello Roesler. Evaluation of safety and effectiveness of NAD in different clinical conditions: a systematic review American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2024 326:4, E417-E427 https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpendo.00242.2023
McReynolds MR, Chellappa K, Baur JA. Age-related NAD+ decline. Exp Gerontol. 2020 Jun;134:110888. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2020.110888. Epub 2020 Feb 22. PMID: 32097708; PMCID: PMC7442590. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7442590/
Izabelle de Mello Gindri, Gustavo Ferrari, Luiz Paulo S. Pinto, Juliana Bicca, Isis Kelly dos Santos, Darlan Dallacosta, and Carlos Rodrigo de Mello Roesler, Evaluation of safety and effectiveness of NAD in different clinical conditions: a systematic review. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2024 326:4, E417-E42 https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpendo.00242.2023
Zhiyuan Gong, Yangxi Cheng, Rui Deng, Ying Zhou, Dan Yu, Cheng Chen, Yingjie Wang, Huiyong Zhu,A crucial role of KLF2-regulated mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in maintaining the stemness of mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, Cell & Bioscience, (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-025-01501-y https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056589
Ready to get treatment? Contact us to book an appointment today!
IV therapies can be booked and administered same day, while more intensive treatments require a pre-screening consult with Dr. Dula to determine the best course of treatment for your body’s specific needs.
Not sure what to do next? Give us a call at 828-237-1511, or email us at wellness@invigorateasheville.com and we’ll get you taken care of!
